Lifecyle
You can easily access and consume Runtimes from various interfaces, including JupyterLab, the CLI or VS Code.
Read below to learn more about the available Runtime Actions.
- Launch.
- List.
- Assign.
- Execute Code.
- Interrupt.
- Restart.
- Pause.
- Resume.
- Transfer State.
- Terminate.
 Launch a Runtime
Launch a Runtime
Launching a Runtime is the first step to unlock the power of Datalayer.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
You can launch Runtimes from the "Runtimes" tab.
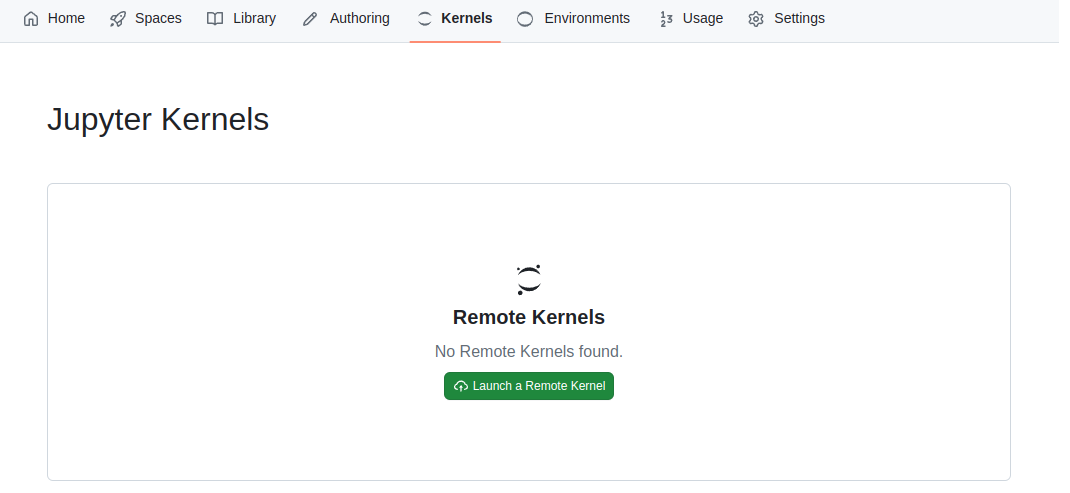
You will be prompted to select a few options:
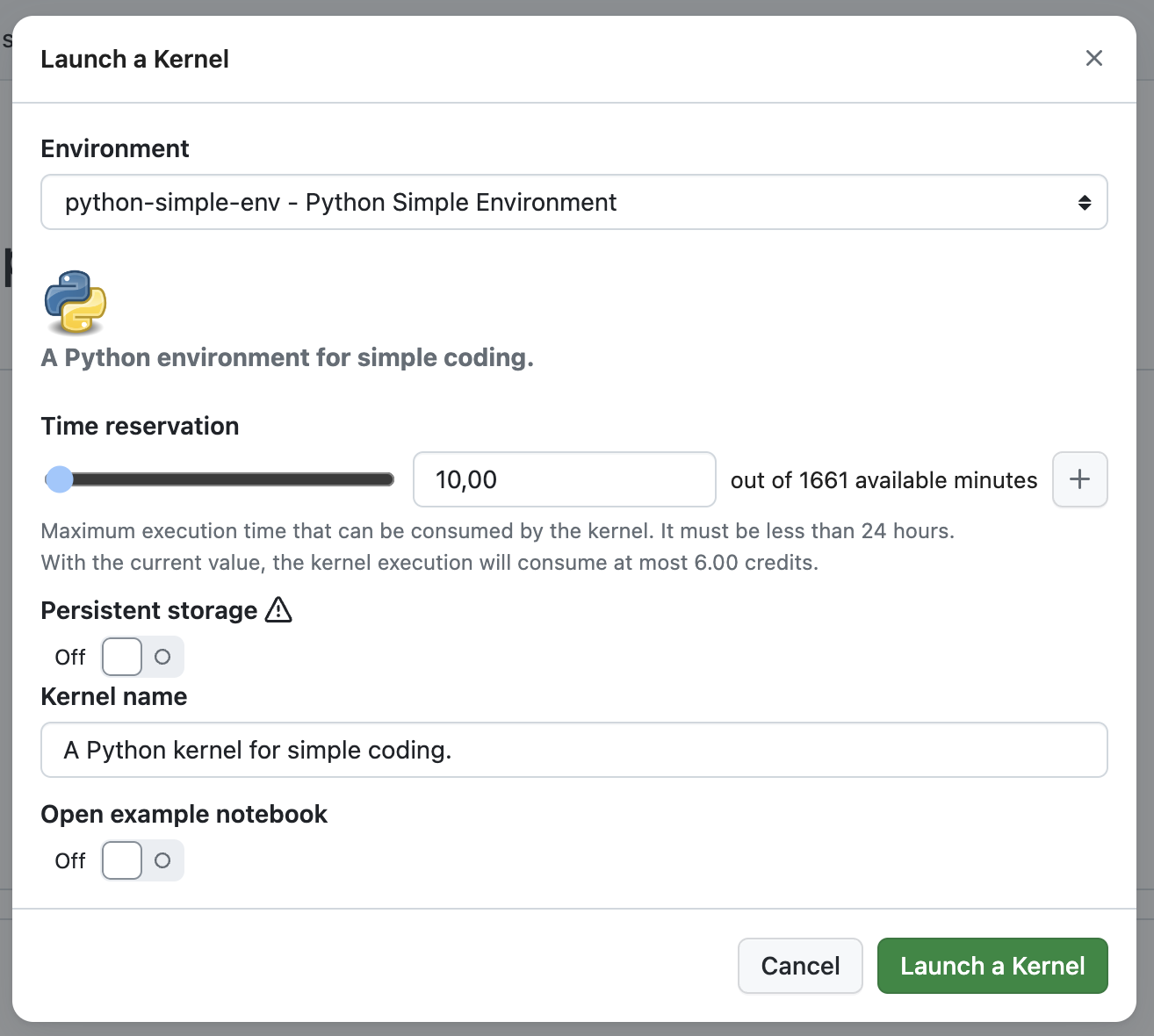
An Environment, this can be a Platform or a User Environment.
For Runtime, a
Time Reservationthat defines the maximum execution time for the Runtime. After this time, the Runtime will be automatically terminated to prevent overconsumption of Credits.You can choose whether the Runtime will have access to persistent persistent storage, allowing data to be retained between Runtime Sessions. Note that Runtimes with persistent storage may take longer to start (approximately 15 seconds instead of 3 seconds). Persistent storage is available under the
~/persistentdirectory on the Runtime.You can also open an example Notebook when the Runtime starts. This feature provides a ready-to-use notebook, helping you quickly familiarize yourself with the environment and start working right away.
You can launch Runtimes from the "Home" page of the extension.
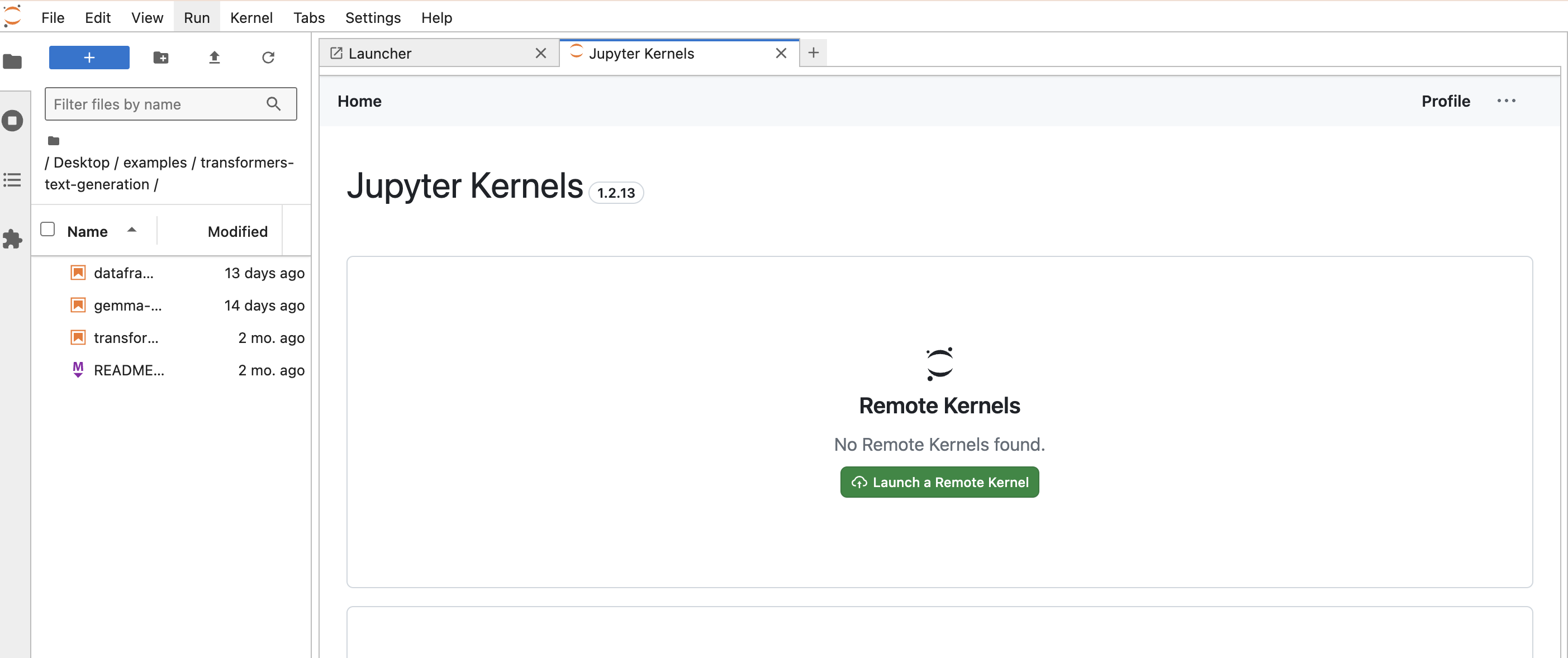
You will be prompted to select a few options:

An Environment, this can be a Platform or a User Environment.
For Runtimes, a
Time Reservationthat defines the maximum execution time for the Runtime. After this time, the Runtime will be automatically terminated to prevent overconsumption of Credits.You can choose whether the Runtime will have access to persistent storage Content, allowing data to be retained between Runtime Sessions. Note that Runtimes with persistent storage may take longer to start (approximately 15 seconds instead of 3 seconds). Persistent storage is available under the
~/persistentdirectory on the Runtime.You can also open an example Notebook when the Runtime starts. This feature provides a ready-to-use notebook, helping you quickly familiarize yourself with the environment and start working right away.
Use datalayer runtimes create ENV_ID --given-name GIVEN_NAME --credits-limit CREDITS_LIMIT.
datalayer runtimes create python-simple-env --given-name k1 --credits-limit 3
Jupyter Runtimes
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Runtime ID ┃ Runtime Name┃ Environment ┃ Expired At ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ jupyter-01j2m0zt2kaheyy3yzn021g032 │ k1 │ python-simple-env │ 2024-08-10T17:29:19.355000+02:… │
└────────────────────────────────────┴──��───────────┴───────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────┘
 List the Runtimes
List the Runtimes
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
You can view the list of running Runtimes in the "Runtimes" tab.
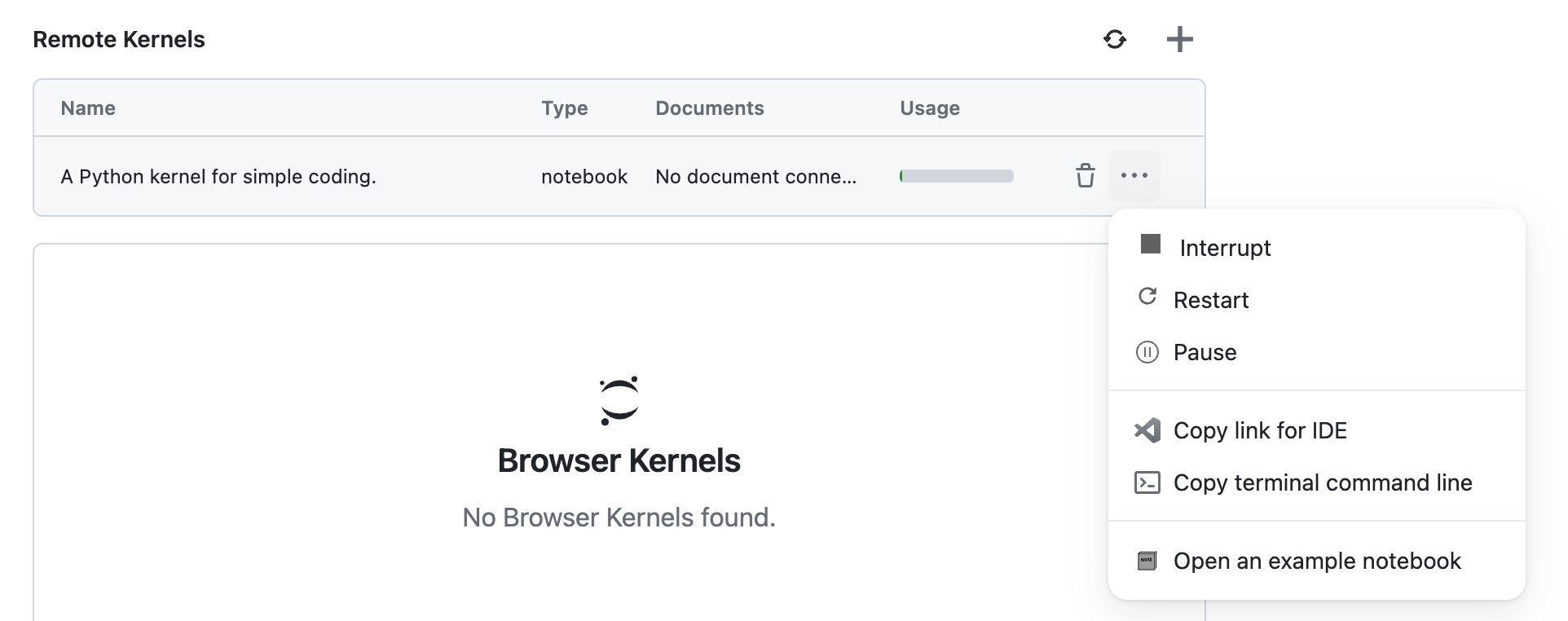
You can view the list of running Runtimes in the "Home" page of the extension.

Use datalayer runtimes list to list all the running Runtimes.
datalayer runtimes list
Jupyter Runtimes
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━�━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Runtime ID ┃ Runtime Name┃ Environment ┃ Expired At ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ jupyter-01j2m0zt2kaheyy3yzn021g032 │ k1 │ python-simple-env │ 2024-08-10T17:29:19.355000+02:… │
│ jupyter-01j2m1kc0zgq3kjcne4p5avhd8 │ k2 │ python-simple-env │ 2024-07-27T06:52:44.704000+02:… │
└────────────────────────────────────┴─────────────┴───────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────┘
 Assign a Runtime
Assign a Runtime
Once your Runtime is up and running, you can assign it to a Notebook or a specific cell.
Assign a Runtime to a Notebook
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- VS Code
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
You can change the Runtime of any Notebook to a Runtime by using the Runtime Picker. The Runtime Picker is located in the top-right corner of the Notebook interface.
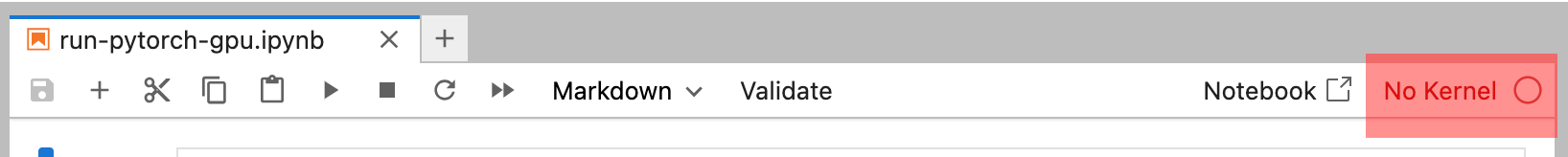
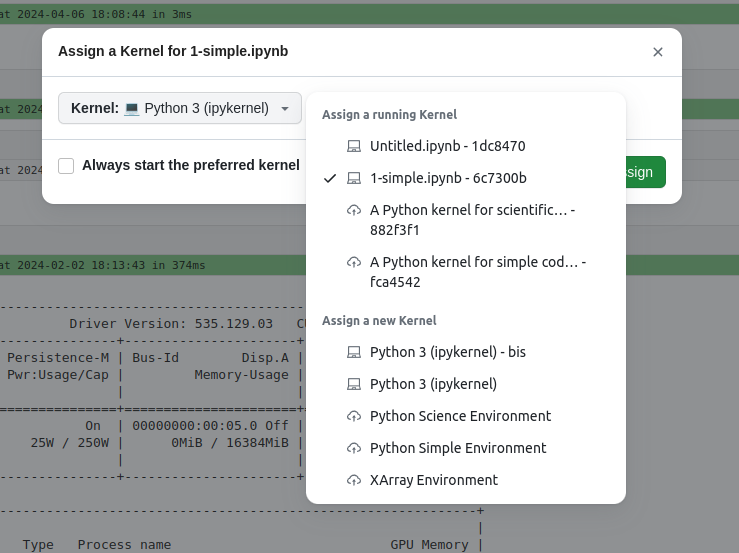
You can also launch a new Runtime directly from the Runtime Picker by selecting an environment in the 'Assign a new Kernel' section. You'll have the option to configure the Runtime settings, such as Time Reservation.
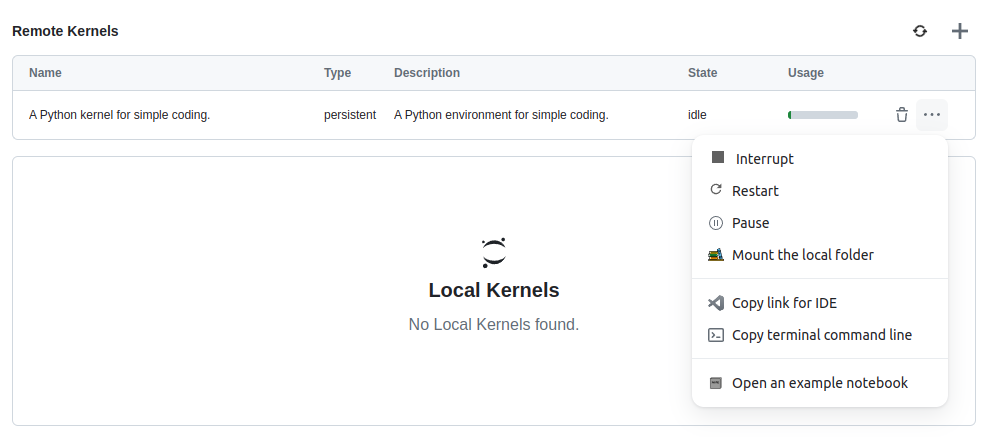
In the SaaS, go to the action menu of the Runtime and select the Copy link for IDE action.
This will copy in your clipboard a link to use in VS Code.
Go to your VS Code Jupyter Notebook, click on the Select Kernel button.
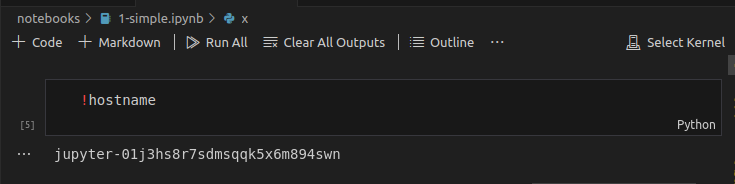
Choose Existing Jupyter Server, next paste the link you have previously copied, click Enter and choose the Python3 kernel.
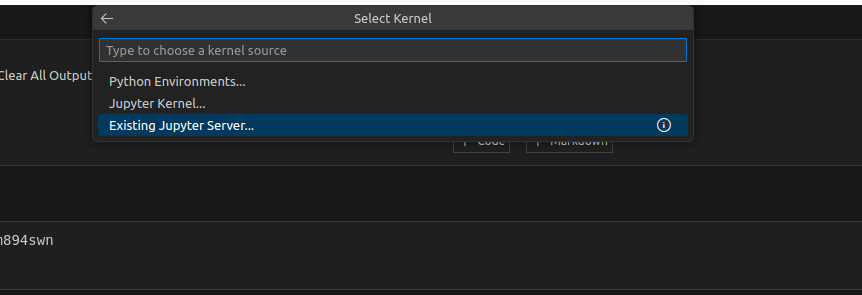
That's it, your VS Code Notebook is connected to your Runtime 👍.
You can connect to a Runtime from other IDEs like PyCharm as explained on the official PyCharm documentation.
🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
Assign a Runtime to a Cell
Datalayer allows you to selectively run specific Notebook cells on Runtime. This hybrid approach optimizes both performance and cost by using Remote resources only when necessary.
Learn more about this feature in our Blog Post.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
To assign a cell to a Runtime, simply use the cell menu as shown below.
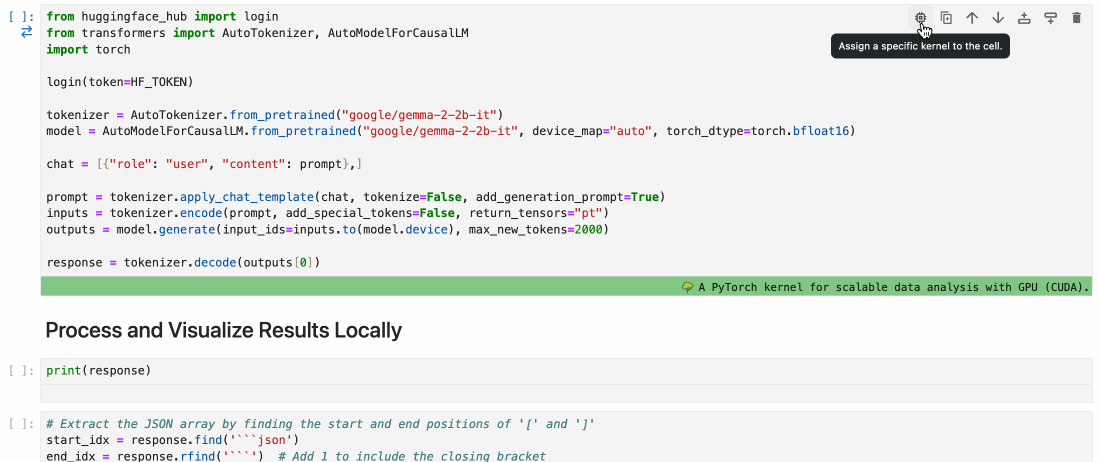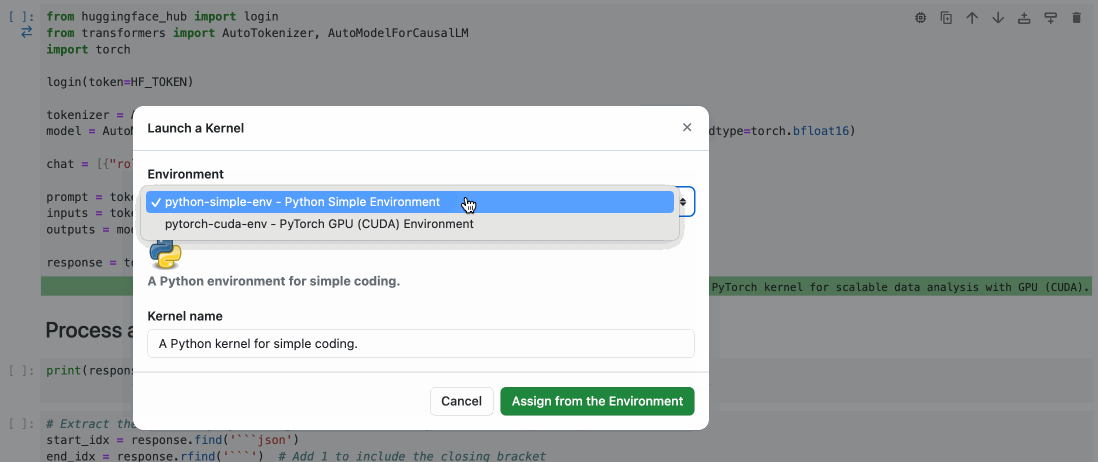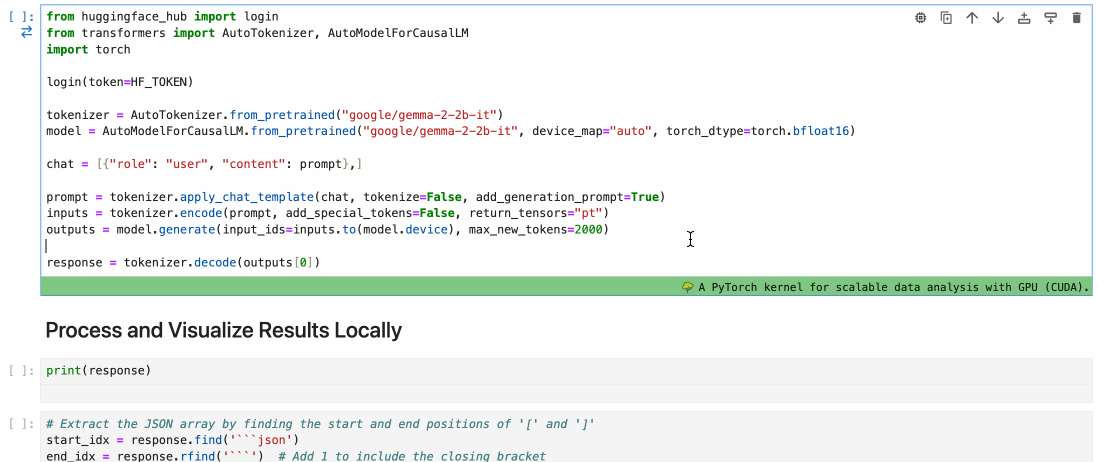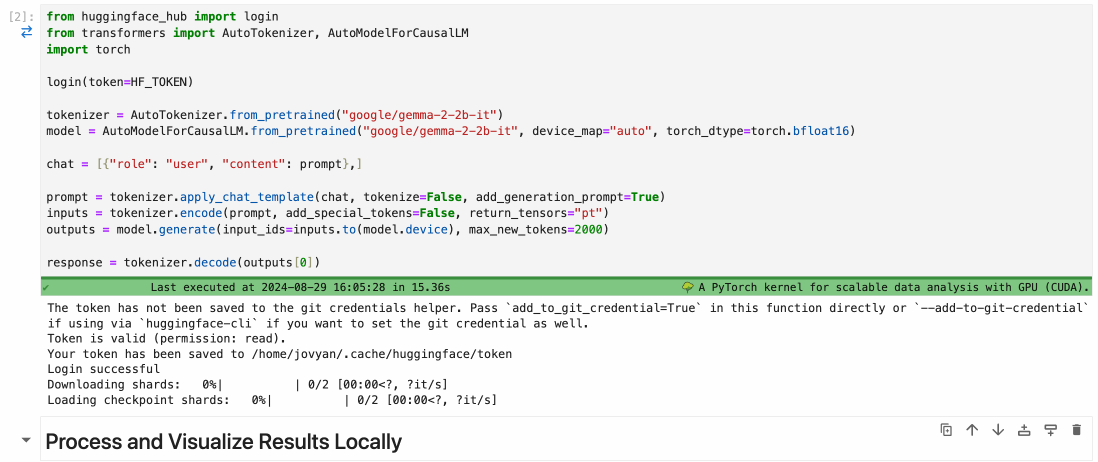
🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
 Execute Code
Execute Code
Execute a Notebook
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- VS Code
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
To execute a notebook on the Runtime, you can use the JupyterLab interface.
To execute a notebook on the Runtime, you can use the VS Code interface.
Use datalayer runtimes exec NOTEBOOK_PATH with the following command options:
--runtime- Runtime ID of the Runtime to use.--raise- Stop the execution one an exception occurred. By default, all cells of the notebook will be executed even if one cell fails.--timeout seconds--verbose- Display all cell outputs. By default, only cell outputs targeting the error stream will be displayed.
datalayer runtimes exec hello.ipynb --runtime jupyter-01j2krcmskpye0sn0nv9a7afhp
Execute a File
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
🚧 JupyterLab is Work in Progress
Use datalayer runtimes exec FILE_PATH with the following command options:
--runtime- Runtime ID of the Runtime to use.--raise- Stop the execution one an exception occurred. By default, all cells of the notebook will be executed even if one cell fails.--timeout seconds--verbose- Display all cell outputs. By default, only cell outputs targeting the error stream will be displayed.
cat > hello.py <<EOF
print('👋 Hello from Runtime')
EOF
datalayer runtimes exec hello.py --runtime jupyter-01j2krcmskpye0sn0nv9a7afhp
rm hello.py
Execute Code in a Console
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
🚧 JupyterLab is Work in Progress
Use datalayer runtimes console --runtime RUNTIME_ID
datalayer runtimes console --runtime jupyter-01j2krcmskpye0sn0nv9a7afhp
[KernelConsoleApp] Datalayer - Version 1.1.9 - Connected as eric on https://prod1.datalayer.run
[KernelConsoleApp] KernelManager using existing kernel server jupyter-01j2krbpy5nh72xcgc8r7jwjh7 expiring at 2024-08-10T17:16:58.139000+02:00
JupyterKernels console 1.1.9
Python 3.11.9 | packaged by conda-forge | (main, Apr 19 2024, 18:36:13) [GCC 12.3.0]
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 8.22.2 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: print('👋 Hello from Runtime')
👋 Hello from Runtime
In [2]:
The Runtime ID is optional. If not provided, it will take the first Runtime found.
To keep the Runtime alive when you exit the console, use CTRL-D or quit(keep_kernel=True).
 Interrupt a Runtime
Interrupt a Runtime
You can interrupt a Runtime by clicking the Interrupt icon. This action will stop the Runtime's current execution.
This is useful when you want to stop a long-running computation or if the Runtime is unresponsive.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI


🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
 Restart a Runtime
Restart a Runtime
You can restart a Runtime by clicking the Restart icon. This action will restart the Runtime, clearing all variables and outputs.
This is useful when you want to start fresh without creating a new Runtime.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI


🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
 Pause a Runtime
Pause a Runtime
You can pause a Runtime by clicking the Pause icon. This action will pause the Runtime, allowing you to resume it later. This is useful when you want to temporarily stop the Runtime, keep its state, and resume it later.
With this feature, you can save credits by pausing the Runtime when you are not actively using it and resuming it when needed without having to rerun all the code that was needed to reach the current state.
When a Runtime is paused, a Runtime Snapshot is created.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI

🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
There are a few limitations to be aware of:
- Object Size Limitations: Extremely large objects, such as massive datasets or memory-heavy models, may exceed persistence limits. Consider external storage options, like cloud storage or databases, for these cases.
- Picklable Objects Only: The Runtime state is serialized using Python's pickle module. While common types (e.g., lists, dictionaries, NumPy arrays) are compatible, some objects (e.g., open file handles, certain class instances) may not be. Review the types of objects in your notebook to ensure compatibility.
 Resume a Runtime
Resume a Runtime
To Resume a Runtime, click the Resume icon of the Snapshot.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI

🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
You can see the pause and resume feature in action below.
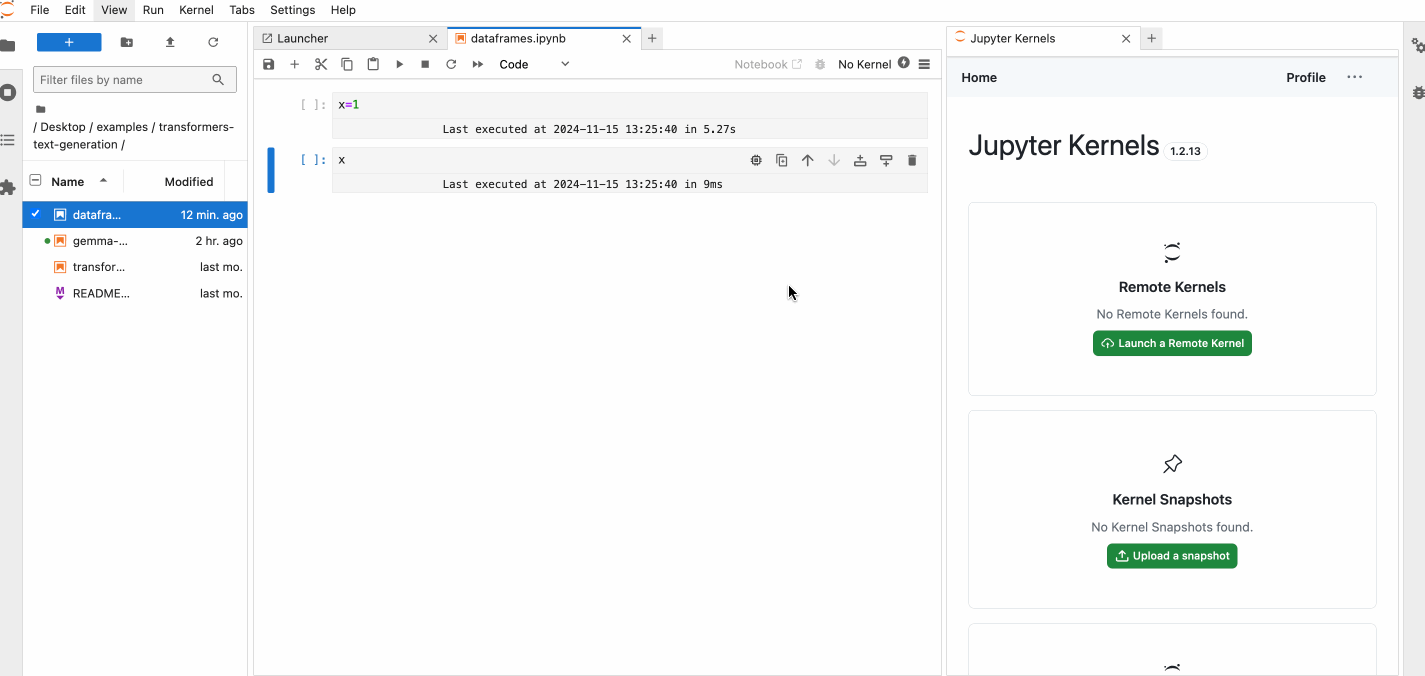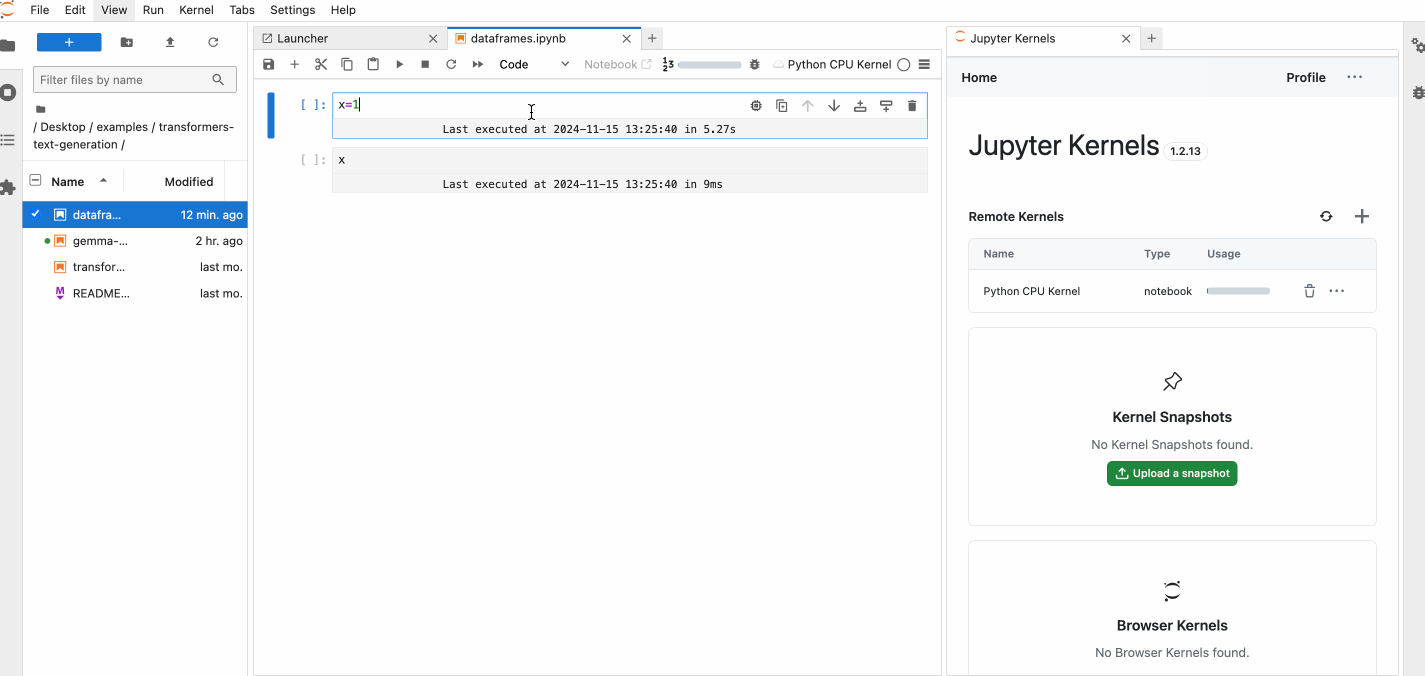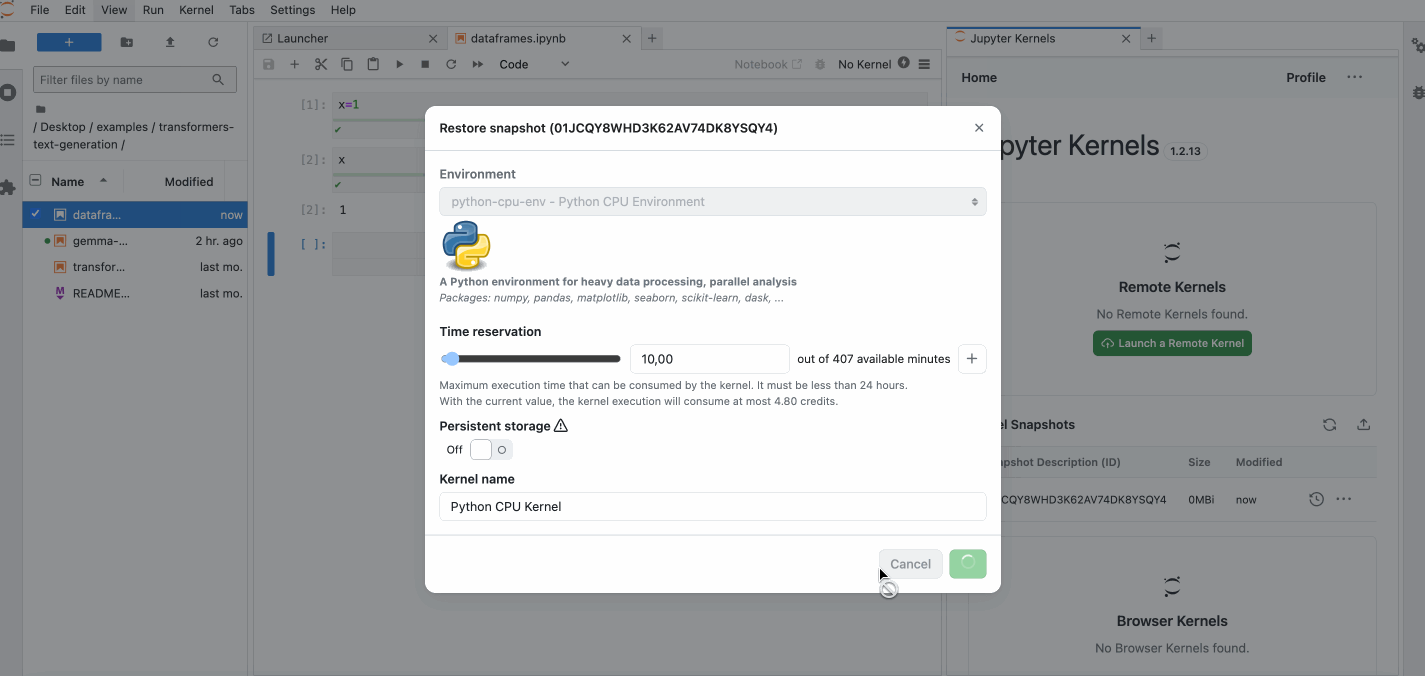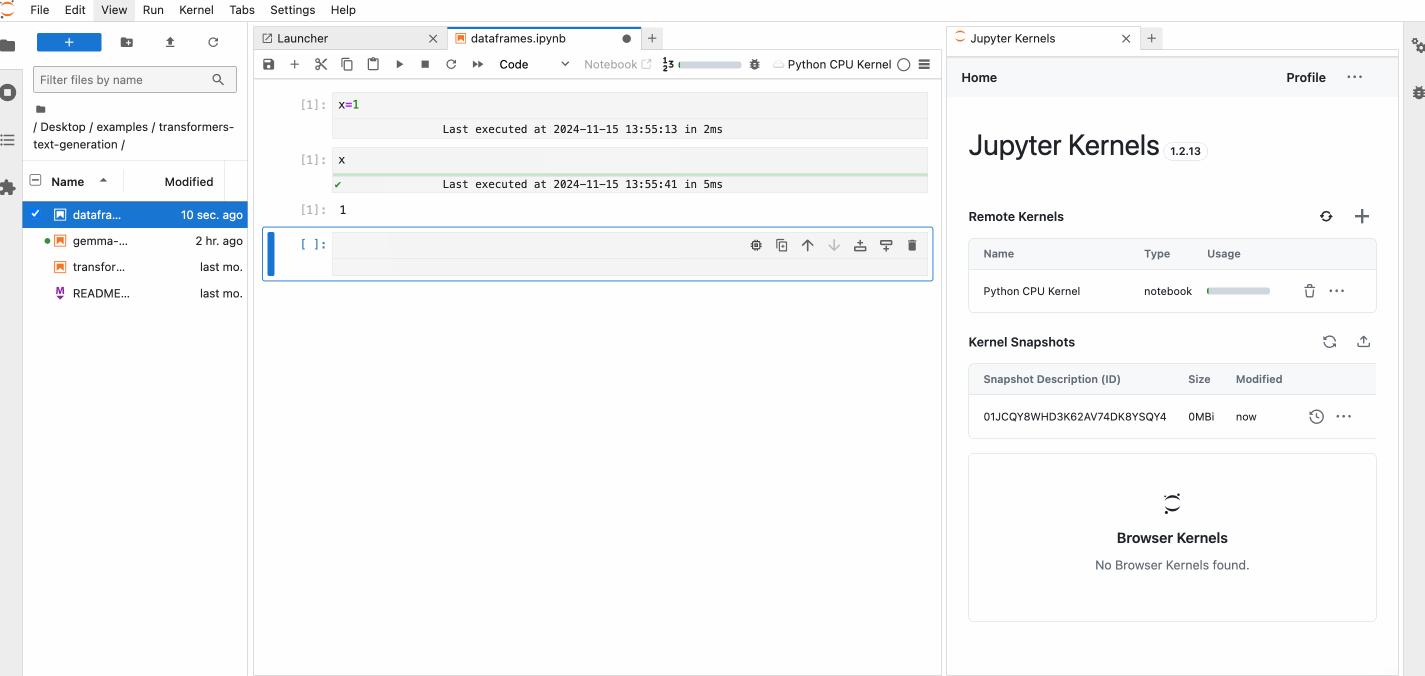
For details on snapshots features, see Snapshots.
 Transfer a Runtime State
Transfer a Runtime State
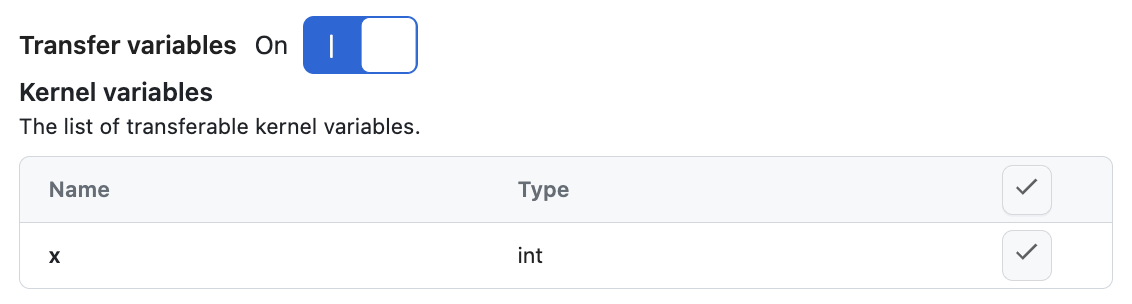
When you switch to a Runtime, you have the option to transfer the variables from the current Runtime to the new one.
This feature is useful when you want to keep the state of your variables when switching Runtimes. This allows to save time and resources by avoiding re-running the code to reach the current state.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress
🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
Variable transfers are currently limited to 7 MB. If you have large variables, consider saving them in the persistent storage. For more information, see Persistent Storage. Additionally, only pickable objects can be transferred.
You can also transfer variables between cells running on different Runtimes. This feature is particularly useful when you want to use variables you defined in previous cells.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI
🚧 SaaS is Work in Progress

🚧 CLI is Work in Progress
 Terminate a Runtime
Terminate a Runtime
You can terminate a Runtime by clicking the trash icon. This action will terminate the Runtime and remove it from the list of running Runtimes. This is useful when a Runtimes is no longer needed.
- SaaS
- JupyterLab
- CLI

Use datalayer runtimes terminate RUNTIME_ID.
datalayer runtimes terminate jupyter-01j2ks4xzbr0vwe8zfzcv5ksm2
[RuntimesTerminateApp] Jupyter Kernels - Version 1.1.9 - Connected as eric on https://prod1.datalayer.run
[RuntimesTerminateApp] Runtime 'jupyter-01j2ks4xzbr0vwe8zfzcv5ksm2' deleted.
This will stop the credits consumption for this Runtime.